As organizations increasingly adopt cloud services, managing the associated costs has become more complex. Cloud cost visibility offers a solution, providing detailed insights into how cloud resources are used and helping businesses optimize their spend.
This blog will explore why cloud cost visibility is important, the main challenges, and the best ways to implement effective cost management strategies.
The Importance of Cloud Cost Visibility
Aligning Cloud Spend with Business Objectives
In today's competitive business environment, it's not enough to simply migrate to the cloud; organizations must ensure that their cloud investments should drive tangible business value. Cloud cost visibility plays a pivotal role in this assessment by providing a clear picture of how cloud resources are being utilized and whether they're contributing to key business objectives.
By gaining visibility into cloud costs, organizations can:
- Identify idle resources that are unnecessarily increasing cloud costs
- Allocate expenses accurately to specific departments, projects, or clients
- Make data-driven decisions about resource provisioning and scaling
- Forecast future cloud spend based on historical trends and planned initiatives
This level of insight enables businesses to optimize their cloud infrastructure, reduce waste, and ensure that every dollar spent in the cloud is contributing to business growth and innovation.
Preventing Cloud Cost Sprawl
There is a phenomenon called "cloud cost sprawl" in cloud computing. This happens when companies lose sight of their cloud resources and the costs associated with them, which can lead to unexpected and sudden cost spikes. Gaining insight into resource usage and costs is essential for managing this issue effectively.
Let’s talk about three common scenarios:
Scenario 1: Idle Resources
These are resources that are running but not being utilized, such as EC2 instances that were launched but are not serving any active workloads.For instance, a company may have set up multiple instances for a project but left them running even after the project has concluded, incurring unnecessary costs.
Scenario:
- 4 EC2 instances (t3.large) created for development
- Project completed in 3 months, and the team moved to a new project
- Instances are left running for the next 3 months until the cost is detected in the monthly bill
- Monthly cost: $140 per instance
- Total waste of 3 months: $1,680
Scenario 2: Underutilized Resources
Underutilized resources refer to instances or services that are running at a significantly lower capacity than what they were provisioned for.For example, an EC2 instance might be sized as an m5.2xlarge, but the actual CPU and memory usage may indicate that a smaller instance, like an m5.large, would suffice, resulting in overspending for the level of service being used.
Scenario:
A team provisions an m5.2xlarge EC2 instance to handle a high-traffic workload that was initially projected.
Over time, the traffic decreases, and the actual usage is consistently under 10% CPU and 20% memory utilization. A smaller instance, like m5.large, would be enough for the current workload.
The company continues paying for the larger instance for 6 months without right-sizing.
- Monthly cost of m5.2xlarge: $384
- Monthly cost of m5.large: $96
- Potential savings per month: $288
- Total waste over 6 months: $1,728
Scenario 3: Non-Critical Workloads Running During Non-Working Hours/Public Holidays
Organizations often run non-essential workloads during hours when they are not actively needed, such as during nights, weekends, or public holidays.For example, a staging environment or other non-critical workloads that run 24/7 can cause unnecessary costs when it could be scheduled to operate only during business hours.
Scenario:
A company maintains a staging environment consisting of 3 EC2 instances (m5.large) to test new features during business hours.
However, the environment is left running 24/7, including weekends and holidays, even though it is only needed from 9 AM to 6 PM, Monday to Friday.- Monthly cost of running 3 m5.large instances 24/7: $432
- Cost of running only during business hours: $108
- Potential savings per month: $324
- Total waste over 3 months of running unnecessarily: $972
By addressing these issues proactively, businesses can prevent minor inefficiencies, ensuring that their cloud environment remains cost-effective.
Note:
At CloudOptimo, our solutions are designed to support organizations in navigating cloud cost challenges:
- CostSaver: Identifies idle, unused, and misconfigured resources, enabling you to eliminate waste and reduce unnecessary costs.
- OptimoSizing: This tool offers rightsizing recommendations, helping organizations optimize their resource usage effectively.
- OptimoScheduler: This tool enables the automation of tasks, ensuring that workloads are only active during work hours, potentially enhancing cost efficiency.
- CostCalculator: Accurately compares, estimates, and identifies cost-effective alternatives for AWS EC2 instances and Azure VMs, allowing organizations to make informed decisions and stay within budget.
Enhancing Financial Governance and Compliance
As regulations become stricter, monitoring finances and maintaining compliance has become essential across all industries. Ensuring that cloud resources are used efficiently and cost-effectively plays a critical role in meeting these requirements. Cloud cost optimization, while primarily focused on reducing unnecessary spending, also helps align with broader financial governance goals by offering greater transparency and accountability over resource usage.
Key regulations where cloud cost optimization plays an indirect but impactful role include:
- Financial Reporting Regulations (GAAP & IFRS): Organizations are required to provide transparent, accurate financial reports. Cloud cost optimization can support this by providing clear insights into resource expenses, helping organizations accurately allocate costs and comply with financial reporting standards like Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) or International Financial Reporting Standards (IFRS).
- Basel III for Financial Institutions: This regulation emphasizes risk management and maintaining adequate capital reserves. By optimizing cloud costs, financial institutions can manage operational costs more efficiently, ultimately helping maintain liquidity ratios and meet the stringent capital requirements set by Basel III.
- Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Regulations: ESG compliance focuses on sustainability, ethical management, and social responsibility. Cloud cost optimization can reduce unnecessary consumption, lower energy use, and shrink an organization’s carbon footprint, thereby supporting sustainability goals and ensuring compliance with ESG-related standards.
Adopting these practices ensures not only financial stability but also helps organizations stay ahead of evolving compliance requirements.
Here’s how good financial practices can help your organization:
- Accurate reporting and budgeting: Having clear information about cloud spending helps create better financial reports and budgets.
- Easier compliance: When you understand your cloud costs, it’s simpler to follow regulations like SOX and GDPR.
- Tracking costs for compliance projects: Knowing where your money goes is especially important when funding compliance initiatives, making it easier to keep track of those expenses.
- Transparency for everyone: Being open about your cloud spending builds trust with stakeholders and auditors by providing clear records.
By focusing on smart cloud cost management, organizations not only save money but also build trust with regulators, investors, and customers.
Driving Cultural Change and Cost Awareness
Perhaps one of the most underrated benefits of cloud cost visibility is its potential to drive cultural change within an organization. When teams have access to clear, actionable cost data, it promotes a sense of ownership and accountability for cloud spending.
This shift can lead to:
- Increased cost consciousness among developers and operations teams
- More collaborative decision-making between IT and finance departments
- A shift towards FinOps practices, where financial and operational considerations are integrated into the development process
- Continuous improvement in cloud resource management and optimization
In the next section, we'll explore the key challenges that organizations face in achieving comprehensive cloud cost visibility, setting the stage for a deep dive into the tools and strategies that can help overcome these obstacles.
Key Challenges in Cloud Cost Management
While the benefits of cloud cost visibility are clear, achieving it is challenging. Organizations often face several obstacles when trying to gain an understanding of their cloud spending:
Complex Pricing Models
Cloud service providers offer many pricing options, including on-demand, reserved instances, spot instances, and various other programs. While this flexibility can lead to cost savings, it also makes it difficult to predict and track expenses accurately. Each pricing model has its own set of rules and conditions, requiring deep expertise to optimize effectively.
Multi-Cloud and Hybrid Environments
Many organizations operate in multi-cloud or hybrid cloud environments, using services from multiple providers alongside on-premises infrastructure. This diversity can lead to siloed cost data and inconsistent reporting mechanisms across different platforms, making it challenging to get an overview of cloud spending.
Dynamic Resource Allocation
The dynamic nature of cloud environments, where resources can be spun up or down rapidly, poses a significant challenge for traditional cost-tracking methods. Autoscaling, serverless computing, and containerization add layers of complexity to resource allocation and cost attribution.
Lack of Granularity in Native Cloud Tools
While cloud providers offer basic cost management tools, these often lack the granularity needed for in-depth analysis. They may not provide detailed breakdowns by team, project, or application, limiting their usefulness for large-scale or complex deployments.
Decentralized Purchasing and Management
In many organizations, different teams or departments have the autonomy to provision cloud resources. This decentralized approach can lead to a lack of oversight and consistency in how resources are acquired and managed, making it difficult to track and control costs effectively.
Data Volume and Velocity
The sheer volume of data generated by cloud usage can be overwhelming. Ingesting, processing, and analyzing this data in real-time to provide actionable insights is a significant technical challenge that requires sophisticated tools and infrastructure.
Skill Gap and Resource Constraints
Many organizations face a skill gap in this area, lacking personnel with the necessary expertise to interpret cloud billing data and implement optimization strategies.
Essential Components of Cloud Cost Visibility
To overcome these challenges and achieve comprehensive cloud cost visibility, organizations need to focus on several key components:
Detailed Resource Tagging
Implementing a robust tagging strategy is fundamental to cloud cost visibility. Tags allow you to categorize resources based on various attributes such as:
- Project or application
- Environment (e.g., production, development, testing)
- Department or cost center
- Owner or responsible team
By consistently applying tags across all cloud resources, you create a foundation for accurate cost allocation and analysis.
- Real-Time Monitoring and Alerting
- Effective cloud cost visibility requires near real-time monitoring of resource usage and spending. This includes:
- Setting up dashboards that provide at-a-glance views of current spend versus budget
- Configuring alerts for unusual spending patterns or when approaching budget thresholds
- Implementing automated responses to cost anomalies, such as shutting down unused resources
Granular Cost Allocation
To truly understand cloud spending, you need the ability to break down costs at various levels:
- By service or resource type
- By project or application
- By team or department
By customer or client (for service providers)
This granularity allows for more accurate budgeting, chargeback, and optimization efforts.
Historical Data Analysis and Forecasting
While real-time data is crucial, historical analysis is equally important for identifying trends and forecasting future spend. Key capabilities include:
- Tracking spending patterns over time
- Identifying seasonal variations in resource usage
- Projecting future costs based on historical data and planned changes
Integration with Financial Systems
To provide a complete picture of IT costs, cloud cost data should be integrated with broader financial management systems. This integration enables:
- Comparison of cloud costs with on-premises infrastructure expenses
- Incorporation of cloud spending into overall IT budgeting and planning processes
- More accurate financial reporting and forecasting
Optimization Recommendations
Advanced cloud cost visibility solutions go beyond reporting to provide actionable recommendations for optimization, such as:
- Identifying opportunities for reserved instance purchases
- Suggesting instance rightsizing based on usage patterns
- Recommending storage tier changes for infrequently accessed data
Achieving Cloud Cost Transparency for Better Cost Management
Cost transparency is the foundational step in any effective cloud cost management strategy. Without detailed insight into where your cloud expenses are allocated, managing resources efficiently is nearly impossible. This is where cost visibility comes into play—providing businesses with the clarity needed to optimize cloud spending and align it with their financial goals.
However, cost visibility is just the beginning. Once a company has achieved full transparency, the next steps—optimization and operation—naturally follow. These stages ensure that cloud resources are used effectively and that costs remain under control in a continuous improvement cycle.
The key stages of cloud cost management can be visualized as a cyclical process, as shown in the flowchart below:
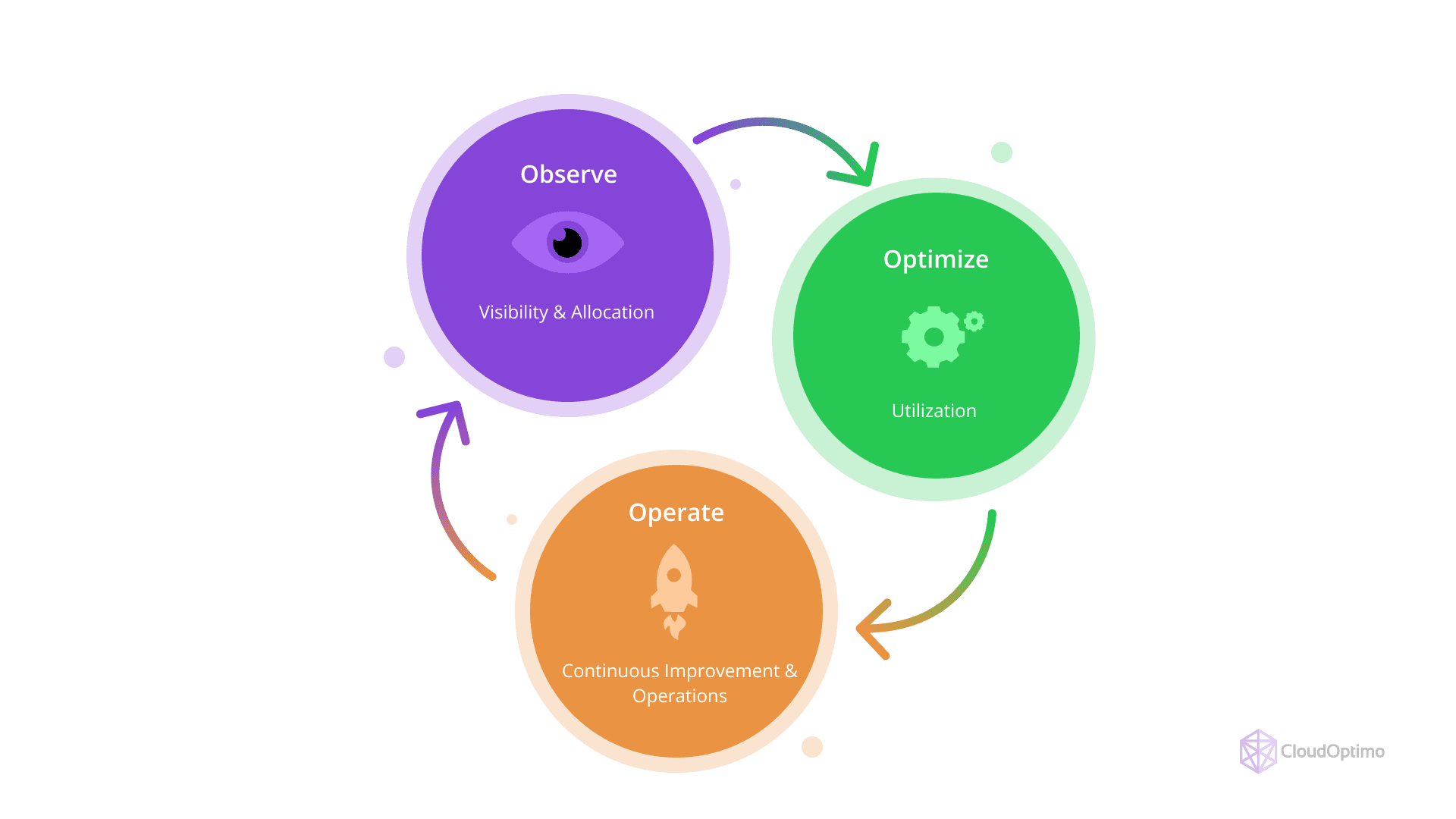
- Observe: Gain full visibility into your cloud spending and allocate resources effectively.
- Optimize: Ensure that your resources are fully utilized to avoid wastage.
- Operate: Continuous improvement and operations to maintain cost efficiency.
This cycle of observe, optimize, and operate enables businesses to achieve not just cost savings but also long-term financial sustainability.
Best Practices
To maximize the effectiveness of cloud cost visibility initiatives, consider the following best practices:
Start with Clear Objectives
- Define what you want to achieve with cloud cost visibility. Is it reducing overall spend, improving budget accuracy, or aligning costs with business value? Clear objectives will guide your implementation strategy.
Implement Comprehensive Tagging
- Develop a tagging strategy that covers all aspects of your cloud infrastructure. Enforce tagging policies through automated tools and governance processes.
Foster a Cost-Conscious Culture
- Educate teams across the organization about the importance of cloud cost management. Encourage a sense of ownership for cloud spending at all levels.
Automate Where Possible
- Leverage automation for tasks such as:
- Resource tagging
- Shutting down non-production resources outside of business hours
- Rightsizing underutilized instances
- Leverage automation for tasks such as:
Regularly Review and Optimize
- Cloud environments are dynamic, and cost optimization should be an ongoing process. Schedule regular reviews of your cloud spend and optimization strategies.
Leverage Reserved Instances and Savings Plans
- Take advantage of discounted pricing options offered by cloud providers for predictable workloads.
Implement Governance and Policies
- Establish clear policies for cloud resource provisioning and management. Use cloud governance tools to enforce these policies automatically.
Real-World Cloud Cost Visibility Success Stories
Case Study 1: E-commerce Giant's Cost Optimization Journey
Organization Profile
- Industry: E-commerce
- Annual Revenue: $500M+
- Cloud Environment: Primary AWS with some Azure services
- Initial Cloud Spend: $8M annually
- Team Size: 200+ developers
Solutions Implemented
- Resource Management
- Automated tagging strategy
- Resource lifecycle management
- Ownership assignment automation
- Cost anomaly detection
- Process Optimization
- Implemented approval workflows
- Set up cost guardrails
- Established regular review cycles
- Created cost optimization team
Results
- 30% reduction in overall cloud spend
- Identified and eliminated $2M in wasted resources
- Improved resource utilization from 35% to 75%
- Achieved 98% tagging compliance
Case Study 2: Financial Services Firm Improves Budget Accuracy
Scenario
- Organization: Global financial services provider
- Environment: Multi-cloud (AWS, Azure, GCP)
- Challenge: Poor budget accuracy and manual cost allocation
- Initial State: 70% budget forecast accuracy, 2-week reconciliation process
Implementation Challenges
- Siloed cloud platforms
- Complex compliance requirements
- Manual cost attribution
- Inconsistent reporting across clouds
Solutions Implemented
- Unified Cost Management
- Centralized monitoring platform
- Automated data collection
- Real-time cost allocation
- Predictive analytics
- Process Automation
- Automated chargeback
- Self-service reporting
- Compliance monitoring
- Budget alerts
Results
- Budget forecast accuracy improved to 95%
- Reconciliation time reduced by 80%
- Implemented accurate departmental chargeback
- Cost allocation accuracy reached 99%
Case Study 3: Global Financial Institution's Multi-Cloud Transformation
Scenario
- Organization: Global bank with operations in 50+ countries
- Environment: Hybrid cloud across AWS, Azure, and on-premises
- Challenge: $50M+ annual cloud spend with limited visibility
Implementation Challenges
- Multiple billing systems
- Complex compliance requirements
- Legacy system integration
Solutions Implemented
- Custom tagging strategy aligned with cost centers
- Automated compliance reporting
- Real-time cost anomaly detection
Results
- 40% reduction in unnecessary spend
- 95% accurate cost allocation
- 60% faster budget forecasting
Future Trends in Cloud Cost Management
As cloud technologies continue to evolve, so too will the approaches to cost management:
AI-Driven Optimization
Machine learning algorithms will play an increasingly important role in predicting cloud usage patterns and automatically optimizing resource allocation.
FinOps Maturity
Organizations will continue to adopt and mature their FinOps practices, integrating financial accountability into DevOps processes.
Sustainability Considerations
Cost visibility tools will expand to include metrics on the environmental impact of cloud usage, helping organizations balance cost optimization with sustainability goals.
Serverless and Container Cost Optimization
As adoption of serverless and containerized architectures grows, cost visibility tools will evolve to provide more granular insights into these complex environments.
With these foundational concepts, challenges, and solutions in mind, organizations can move forward with confidence in implementing their cloud cost visibility strategies.
FAQs
Q: What are zombie resources in cloud cost management?
A: Zombie resources are cloud instances that continue running without being used, leading to unnecessary costs. These can be development environments or test instances left active after project completion.
Q: How can automation improve cloud cost optimization?
A: Automation helps by automatically shutting down unused resources, enforcing tagging, and optimizing instance usage, reducing manual oversight.
Q: What is shadow IT in the context of cloud cost sprawl?
A: Shadow IT refers to the use of cloud resources by departments or teams without the knowledge or control of central IT, which can lead to uncontrolled spending and cloud cost sprawl.
Q: How can historical data analysis improve cloud cost forecasting?
A: Historical data analysis allows organizations to track spending patterns over time, identify seasonal variations, and predict future costs based on past trends. This data helps in budgeting and resource allocation, providing more accurate forecasts and enabling proactive cost optimization.
Q: What are some common challenges in cloud cost management?
A: Some common challenges include complex pricing models, managing multi-cloud or hybrid environments, dynamic resource allocation, lack of granularity in native cloud tools, decentralized purchasing, and the sheer volume of data generated by cloud usage.