Relying on a single cloud provider can limit the full potential of a business’s cloud strategy. While it may offer simplicity at first, organizations often discover opportunities for greater flexibility, cost control, and enhanced performance by exploring more diverse cloud environments. A multi-cloud approach opens the door to tailored solutions that better align with evolving business needs and priorities.
A multi-cloud strategy solves these challenges by distributing workloads across multiple cloud providers, ensuring greater control, resilience, and operational efficiency. Rather than being restricted by the limitations of one vendor, businesses can leverage the best capabilities of multiple providers to improve performance, optimize costs, and strengthen security.
In recent years, global enterprises, financial institutions, and even small businesses rapidly adopted multi-cloud to enhance business continuity, meet compliance requirements, and prepare for future technological advancements.
But what exactly makes this approach so impactful?
In this blog, we will explore seven key benefits of adopting a multi-cloud strategy—breaking down how it enhances business operations, security, and long-term scalability.
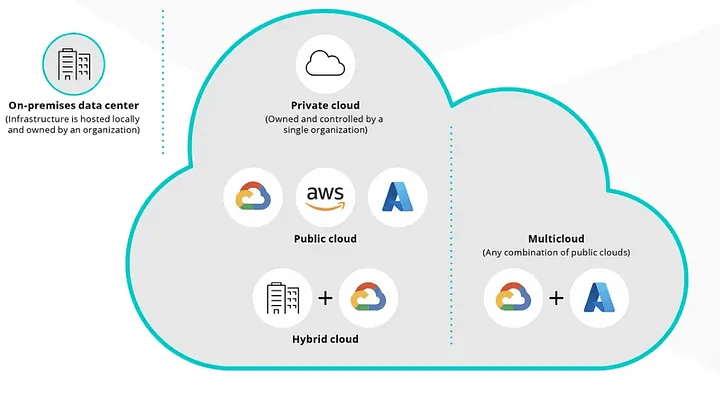
What is Multi-Cloud?
Source - Medium
A multi-cloud strategy is the practice of using multiple cloud service providers—public, private, or a combination of both—to run applications, store data, and manage workloads. Instead of relying on a single cloud provider, organizations strategically distribute their resources across multiple cloud environments to optimize performance, cost, security, and reliability.
How Multi-Cloud Works?
A multi-cloud setup can involve:
- Public clouds (AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure) for scalability and cost efficiency.
- Private clouds for enhanced security and compliance-sensitive workloads.
- Specialized cloud services (such as AI, analytics, or SaaS platforms) to meet specific business needs.
Instead of being tied to a single provider’s limitations, businesses with a multi-cloud approach have greater control over their infrastructure, ensuring they can adapt to market changes, regulatory shifts, and technological advancements with maximum agility.
How does Multi-Cloud Differ from Single-Cloud and Hybrid Cloud?
To understand why multi-cloud matters, let's compare it to other common cloud strategies and see how it addresses unique business challenges that alternative approaches cannot solve.
| Cloud Model | Definition | Key Characteristics |
| Single-Cloud | Using a single cloud provider for all workloads. | Simplified management but leads to vendor lock-in and limited flexibility. |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combining on-premises infrastructure with a public or private cloud. | Offers a balance between traditional IT and cloud solutions but is limited in provider diversity. |
| Multi-Cloud | Using multiple cloud providers for different workloads. | Reduces dependence on one provider, optimizes costs, and improves resilience. |
Unlike hybrid cloud, which focuses on integrating on-premises infrastructure with cloud services, multi-cloud expands beyond a single provider, distributing workloads across multiple cloud platforms to maximize efficiency and minimize risks.
This approach enables organizations to choose the best provider for each specific need, whether for data storage, AI processing, compliance, or disaster recovery, ensuring optimal performance, cost-efficiency, and security.
7 Benefits of Multi-Cloud: A Snapshot
A multi-cloud strategy gives businesses the flexibility to use multiple cloud providers instead of relying on a single one. This approach enhances performance, security, cost efficiency, and resilience, helping organizations adapt to changing business needs. Here’s a quick look at the key benefits:
- Freedom from Vendor Lock-In – Gain flexibility and avoid dependency on a single provider.
- Greater Reliability & Business Continuity – Reduce downtime risks with multiple cloud backups.
- Cost Optimization – Leverage different pricing models to balance cost and performance.
- Stronger Security & Compliance – Maintain security consistency while meeting regulatory requirements.
- Scalability on Demand – Seamlessly expand or reduce resources based on business needs.
- Enhanced Performance & Efficiency – Improve speed and user experience by optimizing workloads.
- Future-Proof IT Infrastructure – Stay ahead with access to the latest innovations and technologies.
By combining the strengths of multiple cloud providers, businesses can build a more resilient, scalable, and cost-effective IT infrastructure. Now, let’s dive deeper into each of these benefits.
Benefit 1: Eliminating Vendor Lock-In for Greater Flexibility
Perhaps the most compelling reason businesses pursue multi-cloud strategies is to avoid becoming overly dependent on a single provider. Vendor lock-in occurs when an organization becomes so deeply integrated with one cloud provider's proprietary services and tools that migrating elsewhere becomes prohibitively expensive or complex.
The Hidden Costs of Single-Provider Dependence
When your entire digital infrastructure relies on one provider, you face several risks:
- Limited negotiating power when contract renewals arise
- Vulnerability to pricing changes or service modifications
- Difficulty adopting innovative technologies from other providers
- Potential disruption if forced to migrate due to service discontinuation
How Multi-Cloud Fosters Agility
By distributing workloads across multiple providers, businesses maintain their freedom to choose. This approach allows you to:
- Select the best provider for each specific workload
- More easily migrate services if a provider no longer meets your needs
- Maintain bargaining power during contract negotiations
- Adapt quickly to changing business requirements
Real-World Example: Netflix, despite being closely associated with AWS, maintains a multi-cloud strategy that includes Google Cloud for certain analytics workloads. This deliberate approach ensures they can leverage specialized capabilities while maintaining flexibility.
Benefit 2: Maximizing Reliability & Business Continuity
Even the largest cloud providers experience outages. In December 2021, AWS experienced significant disruptions that affected thousands of businesses. Organizations with multi-cloud architectures were able to maintain operations by failing over to alternative providers.
The True Cost of Downtime
Cloud outages carry hefty price tags:
- Average cost of downtime for enterprises: $5,600 per minute
- Damage to customer trust and brand reputation
- Lost transactions and revenue opportunities
- Potential contractual penalties for missed SLAs
Building Resilience Through Redundancy
Multi-cloud strategies enable businesses to implement true redundancy:
- Critical applications can be deployed across multiple providers
- Traffic can be automatically rerouted during outages
- Data can be replicated across different cloud environments
- Disaster recovery becomes more robust with provider diversity
Case Study: A major financial services firm implemented a multi-cloud strategy that reduced their overall downtime by 78% in the first year. When their primary provider experienced an outage affecting their payment processing system, their architecture automatically shifted traffic to their secondary cloud provider, maintaining service continuity.
Benefit 3: Optimizing Costs Through Strategic Cloud Utilization
Cloud pricing models vary significantly between providers, and certain workloads may be substantially more cost-effective on one platform versus another.
Understanding Cost Variations
Smart multi-cloud adoption allows businesses to:
- Take advantage of competitive pricing for specific services
- Utilize spot instances and reserved capacity offerings strategically
- Avoid premium pricing for services where you don't need premium features
- Prevent unexpected cost increases by maintaining alternatives
Avoiding Hidden Expenses
Each cloud provider structures their pricing differently, with some charging premium rates for data egress, API calls, or specialized services. By diversifying, you can:
- Select providers with favorable pricing for your highest-volume activities
- Reduce data transfer costs by planning workload placement efficiently
- Take advantage of free service tiers across multiple providers
- Prevent budget overruns by matching workloads to cost-optimized environments
Cost Efficiency Example: One e-commerce company saved 34% on their cloud expenses by moving their data warehousing to Google Cloud while keeping their web infrastructure on AWS. The specialized pricing model for analytics workloads proved substantially more economical for their specific usage patterns.
Benefit 4: Enhancing Security & Compliance Across Cloud Environments
While multi-cloud environments introduce additional complexity from a security standpoint, they also provide unique advantages for risk mitigation and compliance management.
Addressing Multi-Cloud Security Challenges
Effective multi-cloud security requires:
- Centralized identity and access management
- Consistent security policies across providers
- Unified monitoring and threat detection
- Clear understanding of each provider's shared responsibility model
Meeting Regulatory Requirements
Different industries face varied compliance demands, and multi-cloud can help:
- Deploy sensitive workloads in regions with appropriate data sovereignty rules
- Select providers with specific compliance certifications for regulated workloads
- Implement redundancy for systems requiring highest availability
- Maintain separate environments for different compliance frameworks
Security Advantage: By separating workloads across providers, companies create natural security boundaries. This compartmentalization can limit the impact of potential breaches and provide defense-in-depth that's difficult to achieve with a single provider.
Benefit 5: Enabling Seamless Scalability for Business Growth
Different cloud providers excel at scaling different types of workloads. A multi-cloud approach lets you leverage the best scaling capabilities for each application.
Scaling Across Multiple Environments
Multi-cloud strategies support growth by:
- Providing virtually unlimited capacity across providers
- Offering specialized scaling for different application types
- Enabling geographic distribution for global performance
- Supporting both vertical and horizontal scaling approaches
Managing Peak Demands Effectively
Businesses with variable workloads particularly benefit:
- Seasonal retail traffic can be distributed across providers
- Computing-intensive batch processing can be directed to optimized instances
- Development and testing environments can scale independently of production
- Cost-efficient scaling by leveraging each provider's strengths
Scalability Success: A video streaming service uses multiple cloud providers to handle major viewing events. During a popular sports event, they were able to scale to handle 300% of their normal traffic by utilizing capacity across three different cloud providers, something that would have been challenging with a single provider.
Benefit 6: Boosting Performance & Efficiency with Optimized Workloads
Not all cloud services are created equal. Each provider has invested differently in their infrastructure, resulting in performance variations for specific workloads.
Minimizing Latency Through Strategic Deployment
Multi-cloud allows you to:
- Deploy applications closer to users by leveraging providers' global footprints
- Select providers with the strongest presence in your key markets
- Use specialized services optimized for specific workload types
- Balance traffic across regions and providers for consistent performance
Enhancing User Experience
Performance directly impacts user satisfaction:
- Faster page loads and application responses
- More consistent experience during peak usage periods
- Reduced buffering for streaming content
- Improved data processing speeds for analytics applications
Performance Case Study: A global retail application reduced average page load times by 42% by distributing their content delivery across multiple cloud providers, each selected for optimal performance in specific geographic regions.
Benefit 7: Future-Proofing IT Infrastructure for Long-Term Innovation
The cloud computing landscape evolves rapidly, with providers continuously developing new capabilities. A multi-cloud approach positions your business to take advantage of innovations regardless of which provider develops them first.
Multi-Cloud's Unique Innovation Advantages
Unlike single-cloud environments, multi-cloud specifically enables organizations to stay ahead of the technology curve. By distributing workloads across multiple providers, businesses can rapidly adopt cloud-native services unique to each provider without committing their entire infrastructure. This protects against innovation stagnation if a primary provider falls behind competitors in developing new technologies.
One of the most powerful advantages is the ability to combine specialized services from multiple providers into unified solutions. This capability lets organizations leverage the best-in-class offerings from each cloud provider rather than accepting the limitations of a single vendor's portfolio.
Preparing for Emerging Technologies
Multi-cloud strategies create ground for adopting emerging technologies like AI, machine learning, and edge computing. As these technologies mature at different rates across providers, a multi-cloud approach gives your organization flexibility to implement them where they're most advanced.
For instance, serverless architectures and containerization have evolved differently across cloud providers, with each offering unique implementation advantages. Organizations with multi-cloud infrastructure can experiment with these technologies in isolated environments before broader adoption, reducing risk while accelerating innovation.
Innovation Example: A healthcare technology company maintained a multi-cloud strategy that allowed them to quickly adopt a specialized AI service for medical imaging analysis when it became available, without needing to migrate their existing infrastructure. By keeping their data storage and standard applications on their primary cloud while leveraging the specialized AI capabilities of another provider, they accelerated their development timeline by approximately six months.
Creating Your Multi-Cloud Strategy: Practical Considerations
While the benefits are compelling, implementing multi-cloud effectively requires careful planning and consideration of several key factors.
Before You Begin
- Start with your people.
What cloud skills does your team already have? This will heavily influence how and where you deploy first. Multi-cloud success hinges on cross-platform expertise, so figure out where you need to upskill early on. - Get your tools in order.
You’ll need centralized management tools that give you a bird’s-eye view of all your environments. Fragmented tools = fragmented visibility = headaches. - Think data governance.
How will your data move between clouds? Who has access? How will you keep things consistent? Data governance is foundational, so answer these questions upfront. - Rethink your architecture.
Applications that are tightly coupled or performance-sensitive may need to be re-architected to run well across providers. It's not always a lift-and-shift game. - Plan your network.
Reliable, secure, and cost-efficient inter-cloud connectivity is non-negotiable. Pay attention to bandwidth and latency from day one.
Implementation Steps
- Start with a deep dive.
Take inventory of your current workloads. Which ones would benefit from a multi-cloud setup? Some apps might thrive across clouds—others might be better off staying put. - Define clear governance policies.
Document why a workload goes to a particular cloud, not just because it’s technically possible, but because it aligns with business goals. Keep these policies consistent and revisit them as things evolve. - Invest in the right management layer.
Choose tools that unify visibility and control without hiding provider-specific capabilities. Think of it like using a universal remote—you still want to access all the features. - Make security a top priority.
Use a consistent security framework across providers. Zero Trust models are great here—they protect resources no matter where they live, without relying on perimeter-based defense. - Train like you mean it.
Ensure your team understands the ins and outs of every cloud you use. Cross-training boosts resilience and cuts down on knowledge silos.
Multi-cloud isn't simply about using multiple providers—it's about strategically leveraging the unique strengths of each cloud platform to create a more resilient, flexible, and efficient IT environment.
Technical Considerations for Multi-Cloud Architecture
For technical teams implementing multi-cloud strategies, several advanced considerations will help address common challenges and maximize the benefits of your deployment.
Inter-Cloud Networking & Latency Management
Establishing reliable connectivity between cloud environments is fundamental to multi-cloud success. Consider dedicated interconnects between clouds through services like AWS Direct Connect, Azure ExpressRoute, or Google Cloud Interconnect for stable, low-latency connections. These direct links provide consistent performance for data-intensive applications spanning multiple clouds.
Global load balancing solutions using DNS-based or anycast approaches help route traffic efficiently across cloud environments. This not only improves performance but also enables seamless failover during outages. When designing your network topology, minimize "tromboning" of traffic between clouds to reduce latency and unnecessary data transfer costs.
Data transfer optimization techniques become essential in multi-cloud architectures. Implement compression, strategic caching, and CDNs to minimize cross-cloud data movement costs. Consider the trade-offs between data locality, processing requirements, and network traffic when deciding where to place workloads and data.
Data Consistency & Synchronization
Data management presents unique challenges in multi-cloud environments. Carefully choose between eventual and strong consistency models based on your application requirements. Mission-critical applications may require strong consistency, while other workloads can benefit from the performance advantages of eventual consistency.
For databases spanning multiple clouds, consider multi-region deployments with automated replication mechanisms. Solutions like Cosmos DB, Cloud Spanner, and DynamoDB Global Tables offer built-in capabilities for distributed data management. These technologies handle much of the complexity of maintaining data integrity across geographically dispersed environments.
Change Data Capture (CDC) patterns provide reliable mechanisms for data synchronization across environments when real-time database replication isn't feasible. By tracking changes at the source and applying them asynchronously to destinations, CDC helps maintain data consistency without tight coupling between systems.
Orchestration & Automation
The complexity of multi-cloud environments makes orchestration and automation essential for operational success. Kubernetes-based solutions like Google Anthos, Azure Arc, and Amazon EKS Anywhere provide consistent container orchestration across environments. These platforms abstract away provider-specific differences while enabling centralized management.
Infrastructure as Code (IaC) tools such as Terraform or Pulumi allow you to define infrastructure consistently across providers. By representing your entire infrastructure in version-controlled code, you gain reproducibility, auditability, and the ability to implement consistent policies across environments.
For API management in multi-cloud environments, platforms like Apigee, Kong, or AWS API Gateway help create unified API strategies. CI/CD pipelines using Jenkins, GitLab CI, or GitHub Actions with multi-cloud deployment capabilities ensure consistent application delivery across your entire infrastructure.
Security & Identity Management
Zero Trust Architecture principles are particularly valuable in multi-cloud environments, allowing you to implement consistent security policies independent of cloud location. This approach focuses on verifying every access attempt regardless of where it originates, eliminating implicit trust based on network location.
Unified identity management becomes critical when spanning multiple clouds. Consider federated identity solutions like Okta, Auth0, or Keycloak to maintain consistent authentication and authorization across environments. These platforms integrate with multiple cloud providers while providing centralized user management.
Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools like Prisma Cloud or Wiz offer multi-cloud security visibility, helping identify misconfigurations or vulnerabilities across your entire environment. For secrets management, solutions like HashiCorp Vault or AWS Secrets Manager with cross-cloud replication provide secure storage and access to sensitive credentials.
Monitoring & Observability
Comprehensive monitoring across clouds is essential for maintaining visibility and ensuring performance. Unified monitoring platforms like Datadog, New Relic, or Dynatrace provide cross-cloud metrics and insights from a single interface. These tools help identify performance issues regardless of which cloud provider hosts a particular workload.
Centralized logging solutions such as ELK Stack, Splunk, or Sumo Logic aggregate logs from all your environments, simplifying troubleshooting and compliance. Distributed tracing using OpenTelemetry with Jaeger or Zipkin offers end-to-end visibility into requests spanning multiple services and clouds.
Cost management becomes more complex in multi-cloud environments. Specialized platforms like CloudHealth, Flexera, or Apptio provide multi-cloud cost optimization and help identify opportunities for savings across your entire infrastructure.
By addressing these technical considerations thoughtfully, organizations can maximize the benefits of their multi-cloud strategy while mitigating common implementation challenges.